Skip to the content.
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- There’s always the challenge of balancing cost against performance.
Usage meters
- 📝 Used to determine Azure costs for each billing period
- When you provision an Azure resource, Azure creates one or more meter instances for that resource.
- They are charged based on usage
- The meters track the resources’ usage, and generate a usage record that is used to calculate your bill.
- Each meter tracks a particular kind of usage.
- The usage that a meter tracks correlates to a number of billable units.
- Those units are charged to your account for each billing period.
- E.g. when you deploy a single virtual machine:
- Azure might have following meters tracking:
- Compute Hours, IP Address Hours
- Data Transfer In, Data Transfer Out
- Standard Managed Disk, Standard Managed Disk Operations
- Standard IO-Disk, Standard IO-Block Blob Read, Standard IO-Block Blob Write, Standard IO-Block Blob Delete
- 📝❗If you de-allocate a VM you’ll not pay for it. However, your persistent disks remain in your subscription that you pay for.
- Meters and pricing vary per product
- Often have different pricing tiers based on the size or capacity of the resource.
Billing
- At the end of each monthly billing cycle:
- the usage values are charged to your payment method
- the meters are reset
- Check the billing page in the Azure portal:
- summary of your current usage
- any invoices from past billing cycles
Factors affecting costs
Resource type
- Costs are resource-specific
- The usage that a meter tracks and the number of meters associated with a resource depend on the resource type.
- The rate per billable unit depends on the resource type you are using.
Services
- Enterprise, Web Direct, and Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) customers
- Azure usage rates and billing periods can differ between them.
- Some subscription types also include usage allowances, which affect costs.
- Different billing structure apply to products and services from third-party vendors are available in the Azure Marketplace
Location
Bandwidth
- Bandwidth = data moving in and out of Azure datacenters.
- 💡📝 Mostly inbound data (data to Azure) transfers are free.
- Outbound data transfers (from Azure to outside) costs based on Billing Zones
- Moving data between Azure regions counts as outbound data transfer.
Billing zone
- A Zone is a geographical grouping of Azure Regions for billing purposes.
- Each zone has different outbound data transfer prices.
- Zones:
- Zone 1: United States, US Government, Europe, Canada, UK, France, Switzerland
- Zone 2: East Asia, Southeast Asia, Japan, Australia, India, Korea
- Zone 3: Brazil, South Africa, UAE
- DE Zone 1: Germany.
Azure pricing calculator
- Free web-based tool: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/calculator/
- Get estimate costs without deploying and running those services or without manually pricing out each service from the Azure service pricing pages.
- 📝 Can save results in your Azure account, export as Excel or shared as an URL.
- You select Azure services and modify properties and options of the services.
- Outputs the costs per service and total cost for the full estimate
- Modifiable properties:
- Region: E.g. Southeast Asia, central Canada, western United States, northern Europe…
- Tier: E.g. Free Tier, Basic Tier, etc.
- Billing Options: Per type of customers and subscriptions for a chosen product.
- Support Options: Included / paid support options.
- Programs and Offers: Available price offerings according to your customer or subscription type.
- Azure Dev/Test Pricing: Available if subscription is based on a Dev/Test offer.
- On the pricing calculator page, you’ll see several tabs:
- Products. Lists all Azure services, 📝 allows you put together services for your estimate.
- Customizable e.g. for VMs you select region, OS, size, running hours.
- Example Scenarios. Common solutions to add all the components, e.g. VMs + load balancer.
- Saved Estimates. Your previously saved estimates.
- FAQ
Azure Advisor
- Free service that provides recommendations on
- 📝 high availability, security, performance, operational excellence, and cost.
- Analyzes your deployed services and gives personalized recommendations.
- Cost recommendation areas:
- Reduce costs by eliminating unprovisioned Azure ExpressRoute circuits
- Finds circuits that have been in the provider status of Not Provisioned for more than one month.
- Recommends deleting the circuit.
- Buy reserved instances to save money over pay-as-you-go
- Analyzes your VM usage over the last 30 days,
- Determines & shows if you could save money in the future by purchasing reserved instances.
- Shows the regions and sizes where you potentially have the most savings
- Right-size or shutdown underutilized virtual machines
- Monitors your virtual machine usage for 14 days.
- Identifies underutilized virtual machines, allows you to scale down/iin to reduce your costs.
- E.g. VMS with average CPU utilization of <= 5% (adjustable up to 20%)
- E.g. network usage <= 7 MB for +4 days.
Azure Cost Management
- Free tool that for greater insights into costs.
- You can set budgets, schedule reports, and analyze your cost areas.
- 📝 Historical breakdowns of services
- Tracking against budget that’s set
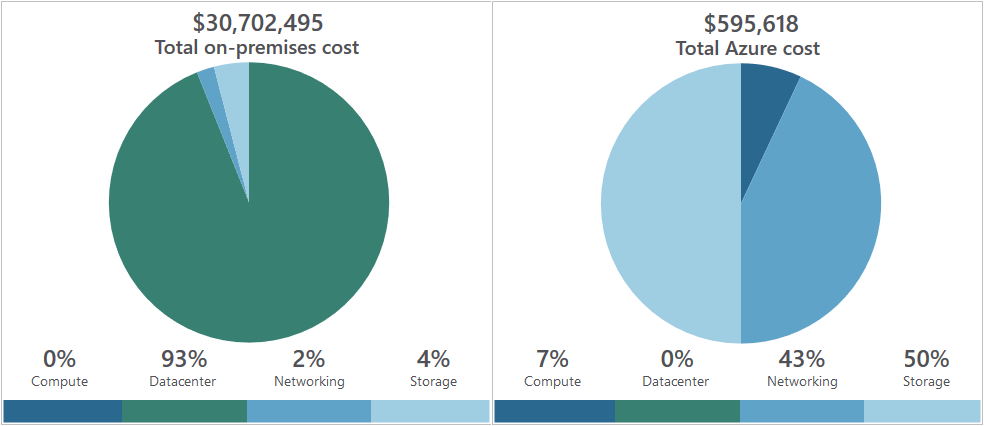
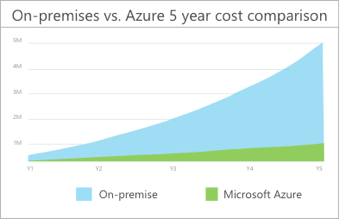
Azure TCO calculator
- Compares on-prem vs cloud costs.
- Describe your infrastructure: servers, databases, storages, networking
- Adjust assumptions: adjust values for e.g. VM costs, electricity costs, IT labor costs.
- Compare costs & see how much you can save
- Web-based tool: azure.microsoft.com/pricing/tco
- TCO = Total Cost of Ownership